Font size:
Print
The endgame in the Russia-Ukraine war
Russia-Ukraine War Endgame: A Breakthrough Moment for Global Diplomacy
Context: As the Russia-Ukraine war enters its fourth year, the conflict has become a protracted geopolitical quagmire with severe humanitarian and economic consequences. With renewed diplomatic efforts, including the revival of the Istanbul peace process and U.S.-led shuttle diplomacy, a fragile endgame appears to be taking shape.
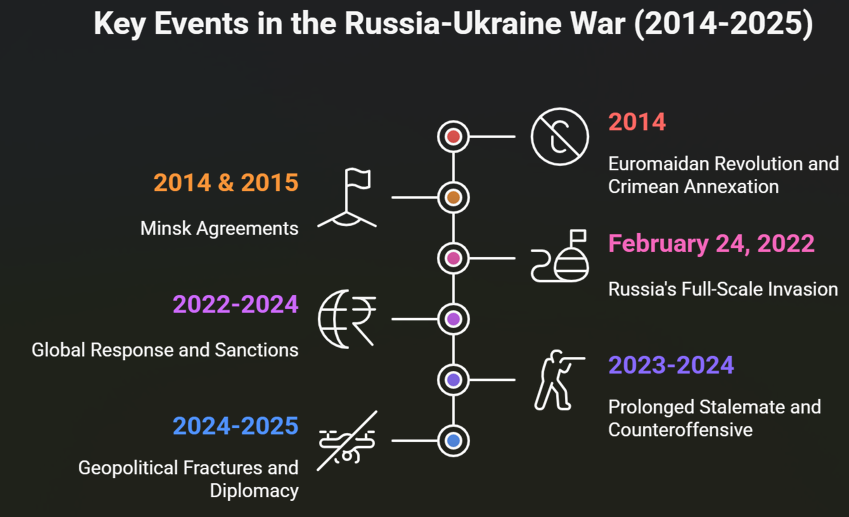
What recent developments have renewed hopes for a diplomatic resolution?
- Revival of the Istanbul Peace Process: Negotiations restarted in May and June 2025, leading to prisoner swaps and tentative ceasefire discussions.
- Trump Administration’s Diplomatic Push: U.S. President Donald Trump’s envoy Keith Kellogg and Secretary of State Marco Rubio initiated direct talks with Russia, framing the war as a “proxy war between nuclear powers” and pushing for a ceasefire.
- Proposed Peace Framework:
- Ukraine: Ceasefire, NATO neutrality, U.S.-backed security guarantees, limited territorial concessions.
- Russia: Recognition of occupied territories, NATO non-expansion, demilitarisation of Ukraine, and sanctions rollback.
- European Role: The U.K. and France are leading a ‘Coalition of the Willing’ for post-war monitoring and confidence-building.
What are the strategic stakes and motivations for key players?
- Russia:
- Seeks to address root causes like NATO expansion and Ukrainian alignment with the West.
- Demands “denazification” and a neutral Ukraine.
- Aims to maintain strategic depth via a “security buffer zone” along the Ukraine border.
- Ukraine:
- Assertive military posture (e.g., Operation Spiderweb drone strikes).
- Seeks Western military and economic support.
- Wants security guarantees without compromising sovereignty or territorial claims.
- United States:
- The Trump administration wants to end the war to reallocate focus on China and West Asia.
- Keen to avoid further reputational and fiscal costs.
- Initiated talks on denuclearisation, linking them to the expiry of the NEW START Treaty (2026).
- Europe and NATO:
How has drone warfare and escalation shaped the conflict dynamics?
- Ukrainian drone strikes (e.g., on Russian bases, bridges, and near Putin’s convoy) have blurred the line between conventional and hybrid warfare.
- Russia’s response: Intensification of attacks to create a border buffer zone and direct threats of full-scale war.
- Escalation risks: Russia’s nuclear doctrine allows for retaliation if state sovereignty is perceived to be under existential threat.
What are the risks and limitations of the proposed peace process?
- Irreconcilable Demands:
- Ukraine refuses to accept loss of territory.
- Russia demands permanent Ukrainian neutrality and demilitarisation.
- Western Distrust: Russia views U.S. denuclearisation proposals with scepticism, recalling past strategic traps.
- Proxy Dynamics: Ukraine’s agency is limited due to its dependence on Western intelligence, weapons, and funding.
- Fragile Ceasefire Mechanisms: Any breach could reignite full-scale conflict, especially with cross-border attacks.
What are the implications for global diplomacy and security?
- Erosion of Trust in Multilateral Institutions: The bypassing of the UN framework and use of informal ‘coalitions’ weakens international law norms.
- Nuclear Stability: Talks on nuclear arms control gain urgency, especially with the NEW START Treaty’s impending expiry.
- European Security Architecture: The conflict tests the EU’s strategic autonomy and its ability to act independently from U.S. leadership.
- Rise of Asymmetrical Warfare: Drones and cyber capabilities are now central to modern conflicts, creating blurred battlefronts.
Subscribe to our Youtube Channel for more Valuable Content – TheStudyias
Download the App to Subscribe to our Courses – Thestudyias
The Source’s Authority and Ownership of the Article is Claimed By THE STUDY IAS BY MANIKANT SINGH



