Font size:
Print
Textile Sector Turning out to be Country’s Strength
Context: Ahead of National Handloom Day, PM Modi linked the Swadeshi Movement to India’s rising textile sector, highlighting its role in nation-building. He shared the success story of Kavita Dhawale, whose income tripled through government support for her Paithani saree craft.
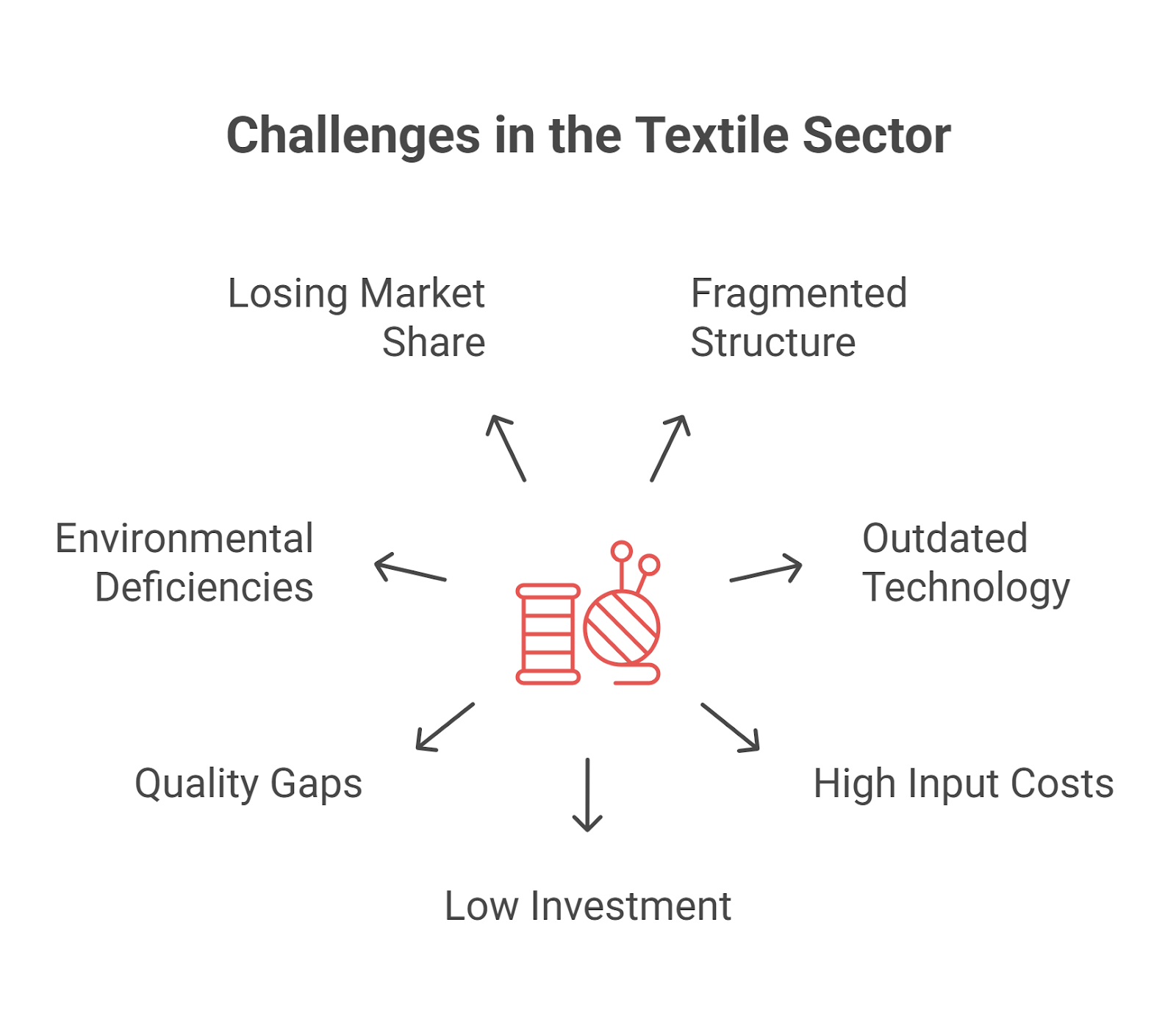
What is the Significance of the Textile Sector in India?
- Substantial Employment: The textile sector is India’s second-largest employment provider after agriculture, offering direct employment to 35–45 million people and supporting the livelihoods of millions more in rural and semi-urban areas.
- Economic Contribution: It contributes 2–4% to India’s GDP, about 12–14% to export earnings, and around 14–20% of industrial production.
- Export Powerhouse: India is the world’s second-largest exporter of textiles and clothing, with exports of $45 billion in 2022, and accounts for approximately one-eighth of export revenues.
- Agriculture Linkages: The sector supports farmers and workers across a diverse value chain—cotton, silk, jute, wool, and man-made fibres—acting as a crucial bridge between agriculture and industry.
- Self-reliant Value Chain: India has a unique, largely self-reliant textile value chain, from raw materials to high-value finished products, supporting various ancillary industries (chemicals, dyes, engineering, packaging).
What are the Government Initiatives to Revamp the Textile Sector?
- PM MITRA Parks: Seven PM Mega Integrated Textile Region and Apparel (MITRA) Parks are being set up (₹4,500 Cr till 2027–28) for world-class, plug-and-play infrastructure to boost competitiveness and attract investment.
- PLI Scheme for Textiles: Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme, outlay of more than ₹10,500 Cr, incentivises high-value manufacturing in MMF and technical textiles, aiming to boost exports and create jobs.
- National Technical Textiles Mission: Drives research, innovation, market development, skill-building, and export promotion in technical textiles.
- SAMARTH (Skill Development): Focused on demand-driven, placement-oriented training to address skills gaps across the textile value chain.
- ATUFS (Technology Upgradation Fund Scheme): Provides capital subsidies to encourage modernisation and adoption of energy-efficient machinery.
- Silk Samagra & Sectoral Schemes: Comprehensive support for the silk sector (Silk Samagra-2), handloom, and handicrafts through cluster development, market promotion, infrastructure, and social security.
- Trade & FDI Policy: 100% FDI via automatic route in textiles, and removal of anti-dumping duties on certain Man-made fibres (MMF) raw materials to enhance availability/cost-effectiveness.
- The Economic Survey 2024-25 has also recommended the augmentation of the production of MMF, as it covers around two-thirds of the overall production and demand globally.
