Font size:
Print
NISAR Earth Observation Satellite
NISAR satellite mounted on GSLV for launch on July 30
Context: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) confirmed on Monday, July 28, that the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) satellite has been successfully mounted, with all launch systems passing final checks.
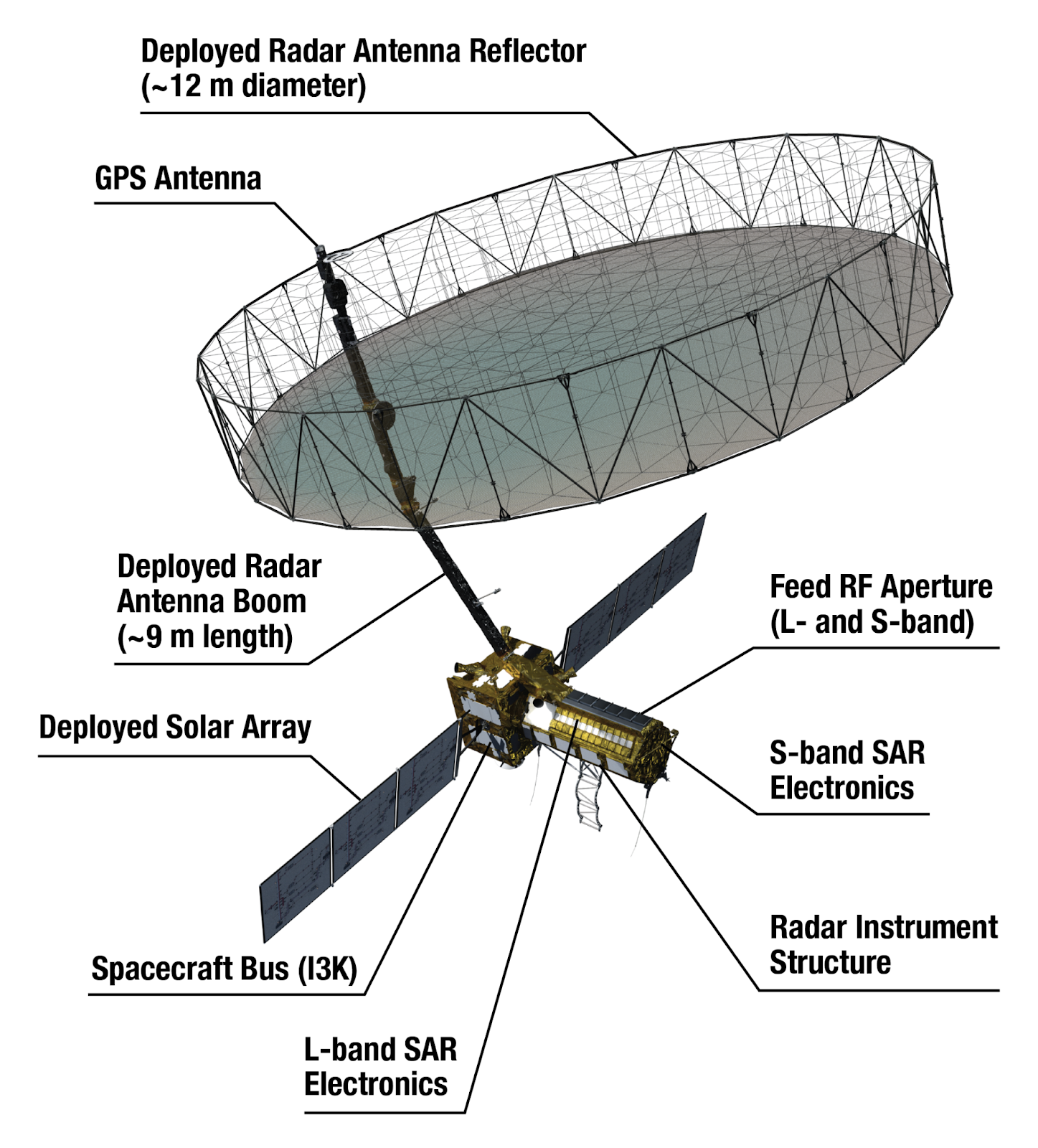
What is the NASA-ISRO NISAR Satellite Mission?
- The 2,392-kg NISAR satellite is a landmark Earth observation mission jointly developed by National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- Scheduled for launch on July 30, 2025, from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, it will be deployed by the GSLV-F16 launch vehicle into a 743-km sun-synchronous orbit.
- NISAR is the first satellite equipped with a dual-frequency Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) – combining NASA’s L-band and ISRO’s S-band radars – mounted on a 12-metre unfurlable mesh reflector antenna.
- The mission, designed for a five-year operational life, is aimed at delivering high-resolution, all-weather, day-and-night global data every 12 days.
What Are the Key Capabilities of the NISAR Satellite?
- NISAR is a next-generation Earth observation satellite with several standout capabilities:
- Dual-frequency SAR Imaging: Enables detailed observation using both L-band and S-band frequencies, improving sensitivity to surface changes.
- High-Resolution SweepSAR Technology: First-of-its-kind deployment to achieve a 242-km swath width, allowing wide-area mapping at high spatial resolution.
- 12-day Global Repeat Cycle: Facilitates timely monitoring of Earth processes such as tectonic shifts or crop growth.
- Day-and-Night, All-Weather Imaging: Operates regardless of cloud cover or lighting conditions.
- Fine Surface Change Detection: Capable of measuring even small-scale ground deformation, ice flow, soil moisture variation, and vegetation dynamics.
What Are the Phases of the NISAR Mission?
- Launch Phase: NISAR will be launched into orbit by GSLV-F16.
- Deployment Phase: A 12-metre radar antenna will be deployed in space using a complex multistage boom mechanism, extending about nine metres from the satellite.
- Commissioning Phase: Lasting for 90 days post-launch, this phase focuses on: Initial checks and calibrations of spacecraft systems. Engineering payload and instrument testing by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).
- Science Operations Phase: Spanning the five-year mission life, this phase will involve: Maintaining the satellite in its science orbit. Conducting extensive calibration and validation. Implementing scheduled orbital manoeuvres to avoid conflicts during data collection.
Why is the NISAR Mission Significant for Global Earth Observation?
- Global Collaboration with Cutting-Edge Tech: Demonstrates India-U.S. space cooperation, strengthening bilateral ties in space technology and environmental science.
- Rapid Event Response: The mission’s ability to capture and distribute data rapidly (within 1-2 days, and near real-time for emergencies) is transformative for disaster response and preparedness.
- Democratising Science: All NISAR data will be freely available to the world, empowering scientists, researchers, and policymakers everywhere, especially in developing nations lacking such observational capacity.
- Critical for Sustainability: As climate change accelerates, granular, timely, and open data from NISAR enables better risk assessments, policy interventions, and planning for a sustainable future.
