Font size:
Print
Money Laundering Crisis: Powerful Strategies India Must Adopt Now
Money Laundering: Strategic Roadmap for a Safer Financial Future
Context: As per a report in the Rajya Sabha, out of 5,892 money laundering cases taken up by the ED under PMLA since 2015, only 15 have resulted in convictions—highlighting both a low conviction rate and a rising trend in such financial crimes, raising concerns over enforcement effectiveness.
What is Money Laundering and Why is it a Threat to National Security and Economy?
- Money laundering is the process of disguising the illicit origin of money derived from criminal activities such as drug trafficking, terrorism, corruption, or fraud, and projecting it as legitimate.
- Section 3 of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), 2002 defines it as the concealment, possession, acquisition or use of proceeds of crime and projecting them as untainted.
- Recognised as a predicate offence under various UN Conventions: Vienna Convention (1988), UN Convention against Transnational Organised Crime (2000) & UN Convention against Corruption (2003).
-
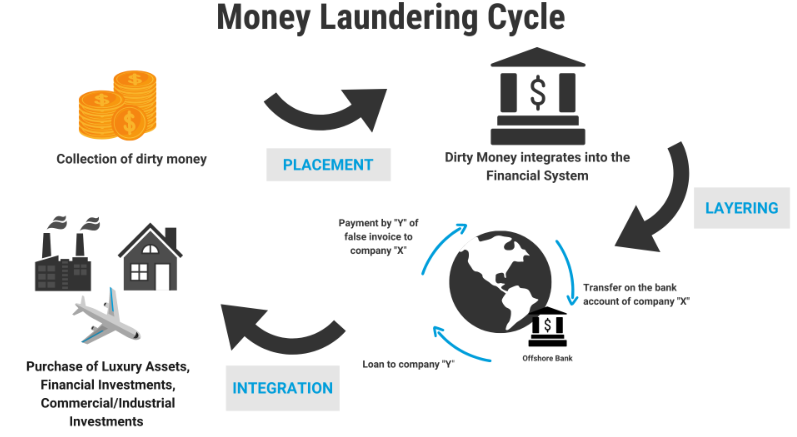
Stages of Money Laundering
-
-
- Placement: Introducing illicit cash into the financial system (e.g., via smurfing or shell firms).
- Layering: Obscuring the audit trail through complex financial transactions (e.g., use of crypto mixers, offshore transfers).
- Integration: Bringing funds back into the legal economy (e.g., real estate, luxury purchases, businesses).
-
-
Threats to National Interest
-
- Terror Financing: Funds insurgency, cross-border terrorism, and extremist activities (FATF notes India as high-risk for ISIL/Al Qaeda-linked financing).
- Economic Instability: Fuels inflation, distorts markets, and undermines monetary policy.
- Loss of Public Revenue: Massive tax evasion reduces funding for welfare schemes.
- Erosion of Institutional Credibility: Hampers investor trust and India’s global reputation.
Who Investigates Money Laundering in India, and What Legal-Institutional Framework Exists?
-
Key Legal Provisions
-
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), 2002: India’s central anti-money laundering law.
- Allows attachment of properties, arrest without FIR, and reversal of burden of proof.
- Defines scheduled offences, prosecution of which can trigger PMLA actions.
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), 2002: India’s central anti-money laundering law.
-
Key Institutions
-
- Enforcement Directorate (ED): Investigates offences under PMLA, empowered to attach assets and file prosecution complaints.
- Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU-IND): Receives, processes, and disseminates suspicious transaction reports (STRs) from banks and financial intermediaries.
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI), SEBI, and IRDAI: Sectoral regulators enforcing AML norms.
-
Judicial Interpretation
-
- Vir Bhadra Singh vs ED (2017): No need for prior FIR to launch PMLA investigation.
- Vijay Madanlal Chaudhary vs Union of India (2022): Upheld stringent PMLA provisions but highlighted procedural safeguards.
-
Global Compliance Mechanisms
-
- Financial Action Task Force (FATF): Intergovernmental watchdog. India is a member and complies with 40 recommendations.
- Egmont Group: India participates in a cross-border financial intelligence exchange.
- Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAA) with 85+ countries: Aid information exchange, asset tracing, and tax evasion detection.
How is India Combating Money Laundering?
-
National Efforts and Measures
-
-
Regulatory Measures
-
-
-
-
- Know Your Customer (KYC), Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) norms for financial institutions.
- Mandatory Reporting: STRs, Cash Transaction Reports (CTRs), and cross-border transfers.
- Use of RegTech: AI-based pattern recognition, UBO (Ultimate Beneficial Ownership) tracing, adverse media screening.
-
- Capacity Building: ED modernisation with forensic labs and inter-agency digital platforms. & Specialised AML/CFT training for officials.
- Digital Ecosystem Strengthening:
-
- Digital public infrastructure (e.g., Aadhaar, UPI) enables traceability.
- Jan Dhan-Aadhaar-Mobile (JAM) trinity aids inclusion and surveillance.
-
-
-
International Cooperation
-
- FATF Mutual Evaluation Report (2024):
- Praises India’s high-level technical compliance and beneficial ownership tracking.
- Commends targeted financial sanctions for proliferation financing.
- Applauds improved digital governance and financial inclusion.
- FATF Mutual Evaluation Report (2024):



