Font size:
Print
Iran–China Relations: A Growing Challenge for India’s Strategic Interests
Iran–China Relations: A Critical Threat to India’s West Asia Strategy
Context: Iran’s attempt to draw China closer through the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) comes at a time of heightened West Asian tensions, following its recent conflict with Israel and looming US–EU snapback sanctions by August 2025.
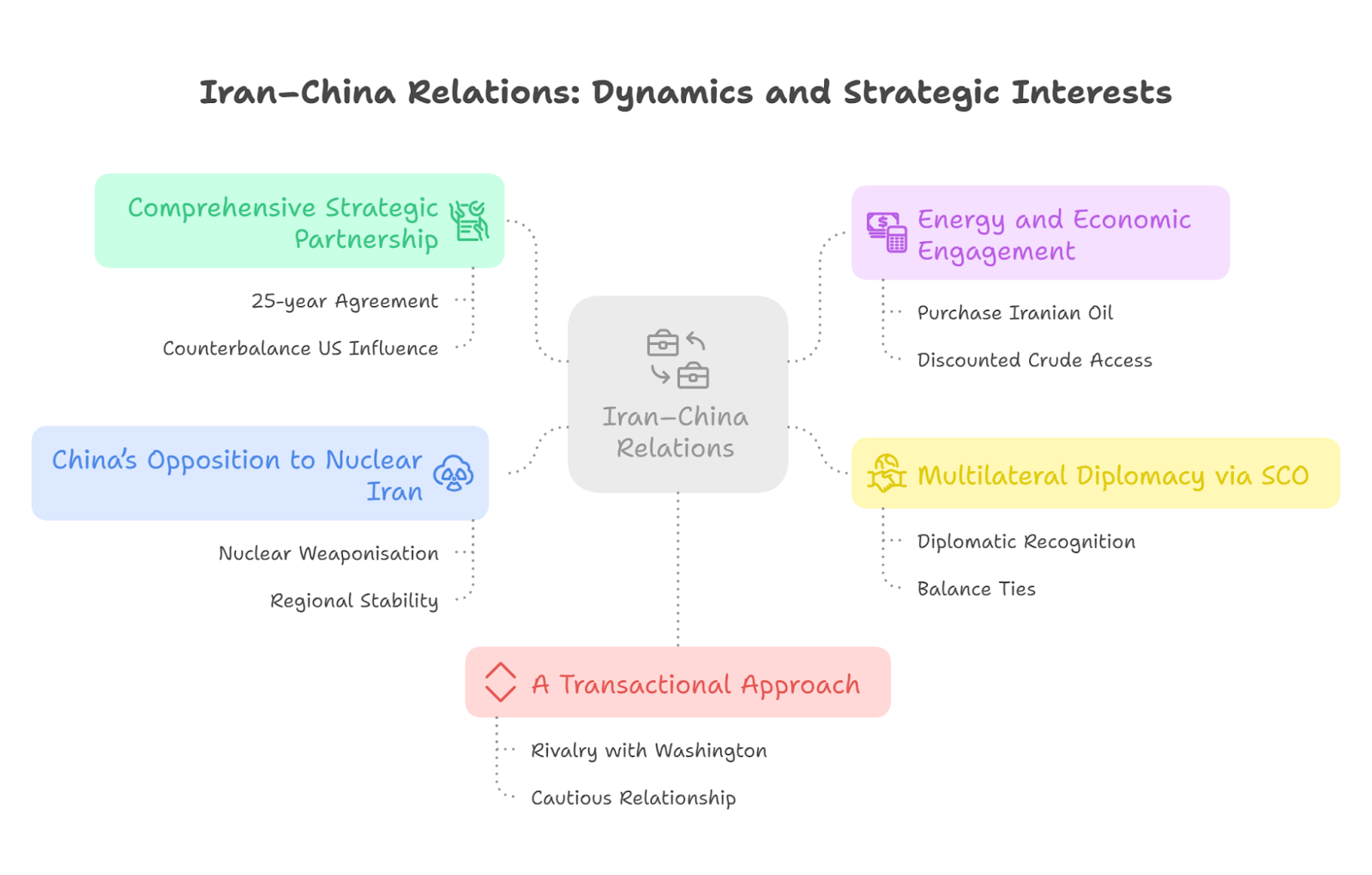
Why are robust Iran–China relations concerning India?
For India, close Iran–China ties carry three major risks:
- Strategic encirclement under BRI: China’s investments in Iran, particularly in the port of Chabahar’s rival Gwadar (Pakistan), and potential involvement in Iran’s energy infrastructure, challenge India’s connectivity goals under the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC).
- Erosion of energy security: India, once Iran’s second-largest oil buyer, had to cut imports due to US sanctions. If China monopolises Iranian crude, India’s diversification of energy sources will narrow.
- Geopolitical imbalance: Strengthened Iran–China ties may marginalise India’s role in West Asia, reducing leverage in forums like SCO and weakening New Delhi’s ability to balance Gulf and Persian interests.
As highlighted in the Economic Survey 2022-23, India’s energy security depends on balancing relations with multiple suppliers; over-dependence on Gulf states without access to Iranian oil exposes vulnerabilities.
What measures have been taken by India to enhance its relations with Iran?
Despite constraints, India has pursued multi-pronged engagement with Iran:
- Chabahar Port Development: India has invested over USD 100 million in the Shahid Beheshti terminal. The port is a strategic alternative to Gwadar and critical for India’s access to Afghanistan and Central Asia. The India–Iran–Uzbekistan corridor (2020) testifies to its utility.
- INSTC Connectivity: India, Iran, and Russia are partners in this 7,200-km corridor linking Mumbai to Moscow. The 2023 trial shipments via Chabahar demonstrated reduced costs and transit time by nearly 40% (Down to Earth report).
- Cultural and Historical Ties: Shared civilisational links, Sufism, and the role of Persian in Indian culture form a soft-power foundation, reinforced through ICCR cultural exchanges.
- Balanced Diplomacy: India engages Iran within its “Link West” policy while maintaining robust ties with Saudi Arabia and Israel, ensuring strategic flexibility.