Hydrogen Fuel in India
India to pilot 600-cr hydrogen fuel infrastructure on highways
Context: India is launching a ₹600 crore pilot project to set up green hydrogen fuelling and repair infrastructure on 10 national highway stretches. Led by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, the initiative aims to test the viability of hydrogen-powered commercial vehicles.
What is H-fuel?
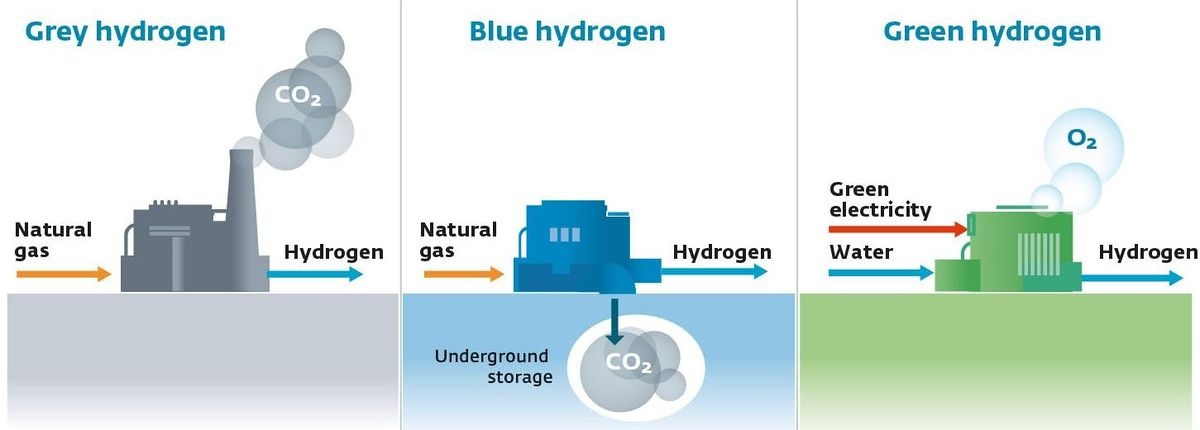
Hydrogen fuel (H-fuel) refers to hydrogen gas (H₂) used as an energy carrier for fuel cells or combustion engines. It is a clean and high-density energy source that can power vehicles, generate electricity, or serve as industrial feedstock. When produced using renewable sources like solar or wind energy, it is termed green hydrogen, making it a crucial pillar of decarbonisation strategies. Types of Hydrogen Fuel:
What are their benefits?
- Environmental Benefits: When used in fuel cells, hydrogen produces only water vapour as a byproduct—no greenhouse gases. It helps reduce air pollution and supports climate goals by replacing fossil fuels.
- Energy Efficiency & Performance: Hydrogen has a higher energy content per unit mass than most fuels, making it powerful and efficient. Hydrogen fuel cells can be refuelled quickly, much faster than charging electric batteries. Vehicles powered by hydrogen can achieve up to 100% better fuel economy compared to gasoline engines.
- Versatility in Applications: Hydrogen can power passenger cars, heavy-duty trucks, industrial processes, and even ports. It can store and deliver energy efficiently, complementing renewable energy sources such as solar and wind.
- Industrial & Economic Advantages: Countries can produce hydrogen domestically, reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels. Hydrogen is already used in refining petroleum and producing ammonia, making it familiar to industry.
- Safety & Sustainability: Unlike fossil fuels, hydrogen doesn’t pose toxicity risks during production or use. It can be produced from natural gas, biomass, nuclear, or renewable energy sources.
How does the utilisation of H-fuels infrastructure help in enhancing India’s energy security?
- Reduced Import Dependency: India imports over 85% of its crude oil, spending nearly $130 billion annually. Hydrogen—especially green hydrogen produced via renewable energy—can replace fossil fuels in key sectors like refining, fertilisers, and transport. This shift reduces exposure to global oil price volatility and geopolitical risks.
- Industrial Decarbonization: Hydrogen can decarbonise hard-to-abate sectors such as steel, cement, and chemicals. These industries are vital to India’s growth and export competitiveness, especially with global carbon border taxes like the EU’s CBAM looming.
- Transport & Mobility Transformation: Hydrogen fuel cells are ideal for heavy-duty transport, railways, and aviation sectors where battery electrification is less viable. Reducing diesel and petrol use in these areas directly cuts import bills and emissions.
- Environmental & Economic Resilience: Green hydrogen helps India meet its climate goals and reduce air pollution. Adds a new pillar to India’s energy mix, alongside solar, wind, and biofuels. Hydrogen production linked to renewable energy can stimulate rural economies through job creation and infrastructure development.
What steps have been taken to augment India’s H-fuels infrastructure?
- National Green Hydrogen Mission: Launched in 2023, it targets 5 million metric tonnes of annual green hydrogen production by 2030. Expected to attract ₹8 lakh crore in investments and create 600,000 clean energy jobs.
- Electrolyser Manufacturing & Refuelling Stations: ₹600 crore pilot launched to focus on long-haul freight and commercial vehicles, where EVs face limitations. India’s first hydrogen refuelling station was inaugurated in Leh in 2024.
- Hydrogen-Powered Trains: India’s first hydrogen-powered train is ready, set to run between Jind and Sonipat in Haryana. Supported by a 1 MW PEM electrolyser producing 430 kg of hydrogen daily. Includes infrastructure for hydrogen production, storage (3,000 kg), compression, and dispensing.
- Hydrogen Diplomacy: India aims to become a global hub for hydrogen production and export, aligning with its net-zero 2070 goals. Strategic diplomacy with Gulf and European nations to establish export corridors.
Subscribe to our Youtube Channel for more Valuable Content – TheStudyias
Download the App to Subscribe to our Courses – Thestudyias
The Source’s Authority and Ownership of the Article is Claimed By THE STUDY IAS BY MANIKANT SINGH