Font size:
Print
Gaza War Threatens IMEC, India’s Vital Connectivity Project
Gaza War Stalls IMEC, India’s Ambitious Trade Corridor Plan
Context: The Gaza war has stalled the India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC), a key connectivity project meant to cut India–Europe shipping time by ~40%, as regional tensions disrupt cooperation among its Middle Eastern partners.
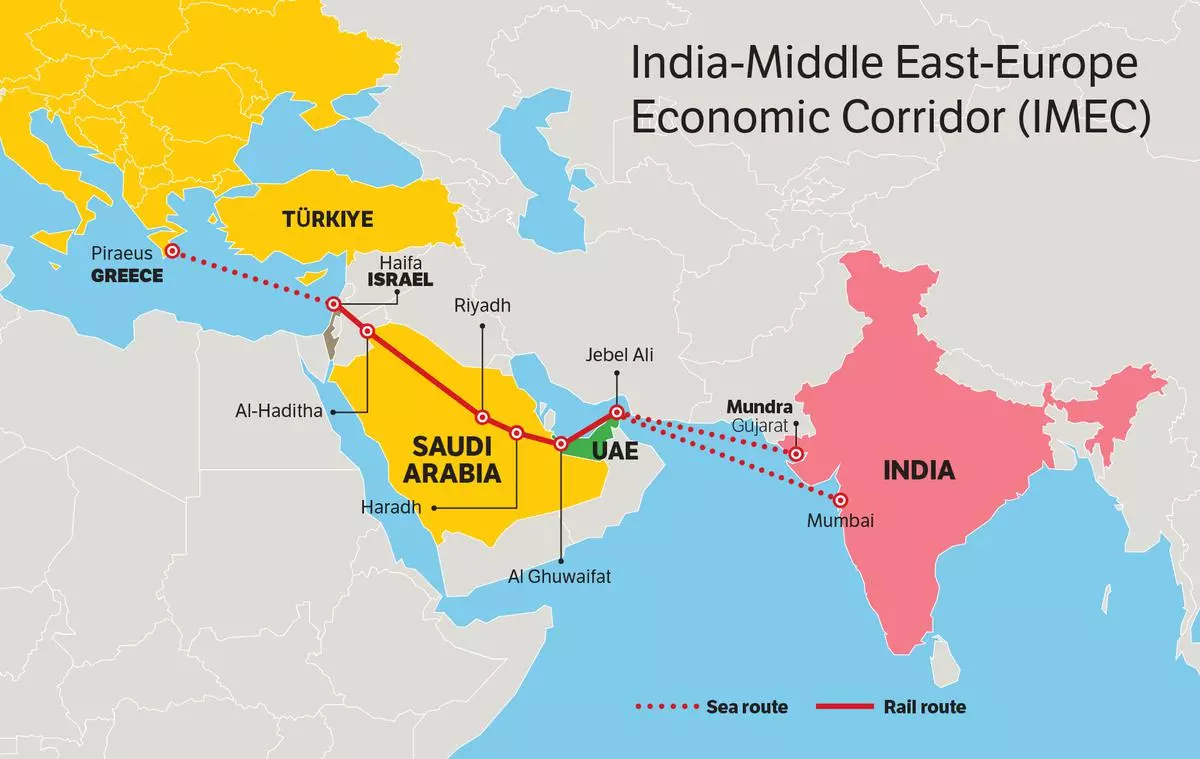
What is the IMEC?
- The India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) is a connectivity initiative announced at the G20 Summit, New Delhi (Sept 2023), linking India, the Gulf, and Europe through integrated infrastructure.
- Two Segments:
-
- Eastern Corridor: India’s west coast ports → UAE (maritime).
- Northern Corridor: UAE → Saudi Arabia → Jordan → Israel (rail) → Mediterranean ports (Greece/Italy) → Europe.
- Planned Infrastructure: Rail freight network, ports, green hydrogen pipelines, undersea electricity & data cables, and logistics hubs.
- Participating Nations: India, US, UAE, Saudi Arabia, France, Germany, Italy, European Commission, and Jordan.
What is the Significance of IMEC?
- Geoeconomic Importance
-
- Cuts India–Europe shipping time by ~40% (compared to Suez route).
- Diversifies supply chains and reduces dependency on chokepoints like the Suez Canal.
- Encourages market-driven, non-debt-trap infrastructure (alternative to China’s BRI). (Economic Survey 2023–24 highlights India’s need for diversified connectivity to avoid external economic shocks).
- Geopolitical Role
-
- Strengthens India–EU–US strategic convergence.
- Enhances Gulf states’ diversification from oil to logistics & green energy.
- Revives India’s historical role as the hub of Spice Route–like trade networks.
- Sustainability Link: Supports renewable energy trade via hydrogen pipelines & electricity cables, aligning with India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission (MNRE, 2023).
How Can IMEC Bolster India’s Strategic Autonomy and Economy?
- Economic Gains
-
- Lower trade costs → improved competitiveness in textiles, chemicals, engineering goods.
- Facilitates FDI inflows in semiconductors, EVs, and green tech manufacturing. (DPIIT data shows logistics cost reduction by 1% of GDP can raise exports by 5–8%.)
- Strategic Autonomy
-
- Provides an alternate route bypassing China-linked chokepoints (e.g., Strait of Malacca).
- Complements PM GatiShakti National Master Plan in integrating ports, rail, and road for global supply chain positioning.
- Strengthens India’s presence in West Asia without exclusive alignment to either US or China—critical for multipolar diplomacy.
What Are Possible Solutions if IMEC Gets Stalled?
- Leverage the INSTC (International North–South Transport Corridor)
-
- Route: India → Iran → Caspian Sea → Russia → Europe.
- Advantage: Bypasses Middle East conflict zones; already operational in parts. (Ministry of Commerce, 2024 report notes INSTC can cut India–Europe freight time by 30–40%.)
- Modular Implementation
-
- Prioritise Eastern Corridor (India–UAE–Saudi) where stability exists.
- Develop digital trade corridors (India–UAE Virtual Trade Corridor model) to sustain integration without full physical connectivity.
- Multilateral Financial Backing
-
- Use G20’s Global Infrastructure Facility & private investments to hedge geopolitical risk.
- Set up an IMEC Secretariat in a neutral Gulf hub for coordination and dispute resolution.



