Font size:
Print
Financial Inclusion Index 2025
Context: The RBI released the Financial Inclusion Index (FI-Index) for March 2025, assigning a score of 67, up from 64.2 in 2024. The index reflects broad progress in financial access, usage, and quality across India.
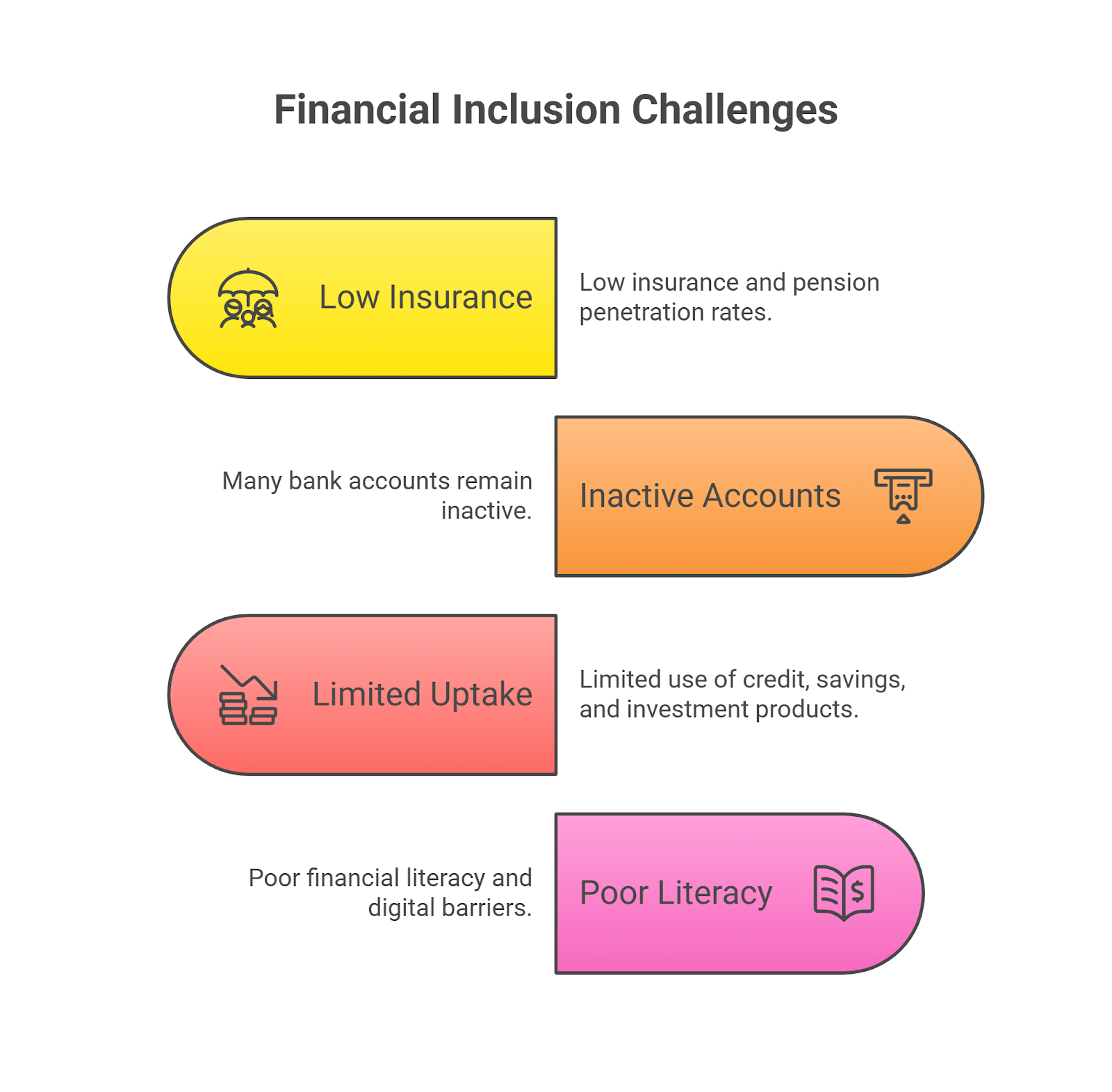
What is the Financial Inclusion Index?
- It is a comprehensive quantitative measure designed to capture the extent of financial inclusion in a country, particularly India.
- It consolidates information across multiple financial sectors such as banking, insurance, investments, pension, and postal services.
- The index is expressed as a single value ranging from 0 to 100, where 0 indicates complete financial exclusion, and 100 indicates full financial inclusion across the population.
What are its major metrics?
The major metrics (parameters) of the Financial Inclusion Index are divided into three broad categories with assigned weightages:
- Access (35%): Measures the availability and physical accessibility of financial services, including the number of bank branches, ATMs, and the presence of various financial products in different regions.
- Usage (45%): Reflects the extent to which individuals and households actively use financial services such as savings accounts, loans, insurance, credit cards, and investment products.
- Quality (20%): A unique feature that assesses the quality of financial services, including consumer protection, financial literacy, and reducing inequalities or deficiencies in service delivery.
How is it different from global parameters?
- The Indian FII is distinct due to its inclusion of a quality parameter focusing on consumer protection, financial literacy, and service inequalities, which is not always explicitly measured in many global indices.
- For instance, the Global Financial Inclusion Index (such as the one developed by Principal or the World Bank’s Global Findex) primarily measures financial inclusion through pillars like government support, financial system support, and employer support, focusing on availability, uptake, and infrastructure of financial services rather than explicitly including quality or literacy metrics.
- Additionally, the index is constructed without a base year and reflects the cumulative efforts of all stakeholders over time rather than year-on-year relative change.
- It also covers a broad spectrum that includes postal services and pension sectors, which may be less emphasised in other global indices.
How does FII help in understanding the inclusive growth in the Indian economy?
- The FII helps in understanding inclusive growth in the Indian economy by providing a comprehensive measure of how well financial products and services reach all segments of society, including vulnerable and remote populations.
- Tracking this index annually allows policymakers and institutions to:
- Monitor progress and identify gaps in financial inclusion.
- Assess the impact of financial inclusion initiatives.
- Guide policy formulation to enhance access, active usage, and quality of financial services.
- Facilitate research linking financial inclusion with macroeconomic variables such as poverty reduction, economic empowerment, and overall economic growth.
- The inclusion of the quality parameter emphasises consumer protection and literacy, which are crucial for sustainable and meaningful inclusion, ensuring that increased access translates into real economic benefits and empowerment for marginalised groups.

