Font size:
Print
Controller General of Accounts: Role, Functions, and Relevance
Context: The appointment of Ms. T.C.A. Kalyani as the new Controller General of Accounts (CGA) comes at a crucial time when India is deepening public financial management reforms through digital governance, real-time fund tracking, and transparency measures, making her role pivotal in ensuring fiscal prudence and efficient delivery of welfare schemes.
Who is the Controller General of Accounts?
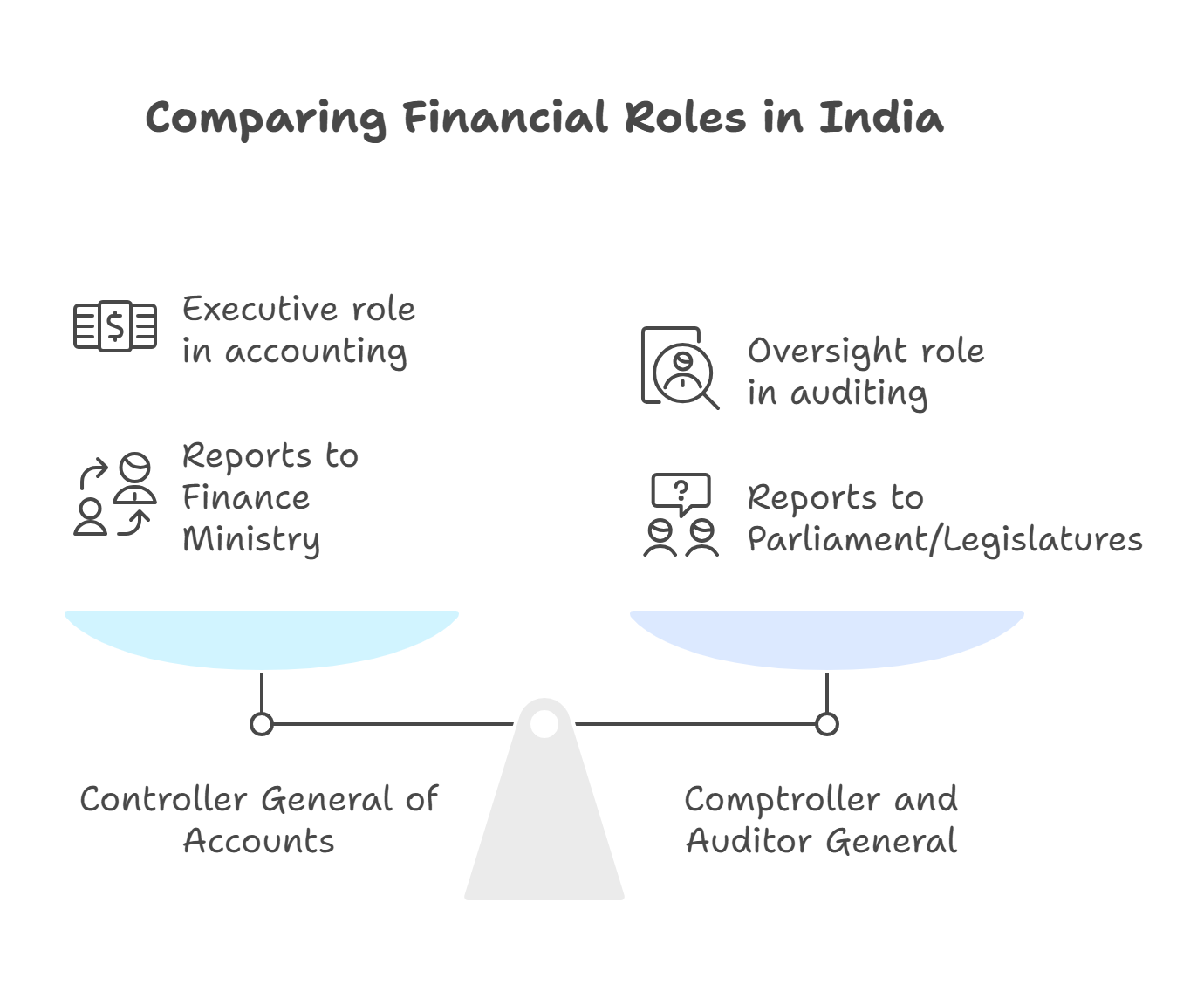
- The Controller General of Accounts (CGA) is the principal accounting adviser to the Government of India and heads the Indian Civil Accounts Service (ICAS). On 1 September 2025, Ms. T.C.A. Kalyani, a 1991-batch ICAS officer, assumed charge as the 29th CGA, succeeding S.S. Dubey (1989 batch).
- CGA operates under the Department of Expenditure, Ministry of Finance, and is entrusted with establishing and maintaining a technically sound management accounting system. The office was created in 1976 (Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) Act), following the separation of accounting and auditing functions of the Union Government.
What are the major functions of the Controller General of Accounts?
According to the Charter of the CGA (Ministry of Finance) and the Economic Survey 2022-23, the CGA performs the following key functions:
- Central Government Accounts: Prepares and submits the annual Union Government accounts to Parliament, ensuring fiscal transparency.
- Expenditure Oversight: Monitors and tracks Union Government expenditure on a monthly basis, aiding fiscal prudence.
- Accounting System Design: Frames rules, procedures, and standards for government accounting and internal audit.
- Financial Management Information System (PFMS): Operates the Public Financial Management System, a platform that integrates real-time fund tracking for centrally sponsored schemes. For instance, PFMS was critical during COVID-19 relief transfers ensuring last-mile delivery (Economic Survey 2021-22).
- Internal Audit: Strengthens accountability within ministries by conducting risk-based audits.


