India’s First GCC Hub: Maharashtra Leads the Way
Maharashtra partners with ANSR to build India’s first Global Capability Centre (GCC) city in Navi Mumbai. Learn how GCCs drive innovation, create jobs, and strengthen India’s global economy.
Context : India’s First GCC
Maharashtra is set to emerge as a premier destination for global enterprises with the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between the state government and ANSR, a global firm specialising in building Global Capability Centres (GCCs). The collaboration aims to develop India’s first dedicated GCC city in Navi Mumbai, following the recent approval of the state’s GCC Policy by the Maharashtra cabinet.
This move positions Maharashtra at the forefront of India’s evolving knowledge economy, aligning with the government’s vision to attract multinational corporations (MNCs), generate employment, and strengthen India’s global business footprint.
What Are Global Capability Centres (GCCs)?
Global Capability Centres (GCCs) are wholly owned offshore units established by multinational corporations to manage strategic, technical, and operational business functions. Unlike traditional outsourcing models, GCCs are integral to a company’s core operations, serving as innovation and capability hubs.
These centres leverage global talent pools and cutting-edge technologies to enhance organisational efficiency, reduce operational risks, and drive digital transformation. Over time, GCCs have evolved from cost-saving back offices into strategic partners contributing directly to business growth, research, and innovation.
Key Functions of GCCs
GCCs are versatile entities that manage a range of complex functions for their parent organisations. The main operational areas include:
-
Research and Development (R&D): Conducting innovation-driven research and developing new products, technologies, and processes.
-
Digital Transformation: Implementing artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and data analytics to modernise global business functions.
-
Finance and Accounting: Managing cross-border financial operations, compliance, and global reporting standards.
-
Human Resources (HR): Handling recruitment, training, and global talent development for diverse markets.
-
Supply Chain Management: Streamlining logistics, procurement, and vendor management across international operations.
By centralising these functions, GCCs enable MNCs to enhance coordination, achieve economies of scale, and accelerate innovation.
GCCs vs. BPOs: The Key Difference
Although Global Capability Centres (GCCs) and Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) units both operate offshore, their purpose and structure differ significantly.
| Feature | GCCs | BPOs |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Fully owned and operated by multinational corporations | Outsourced to third-party service providers |
| Strategic Role | Integral to global business operations | Focused on non-core, support functions |
| Innovation Focus | High – emphasis on R&D and digital transformation | Low to moderate – operational efficiency focus |
| Talent Utilisation | Employs highly skilled, domain-specific professionals | Engages a more general workforce |
| Long-term Investment | Involves significant capital and strategic investment | Typically lower capital expenditure |
While BPOs provide cost-effective services, GCCs act as strategic innovation engines, supporting long-term business sustainability and competitiveness.
Economic Significance of GCCs in India
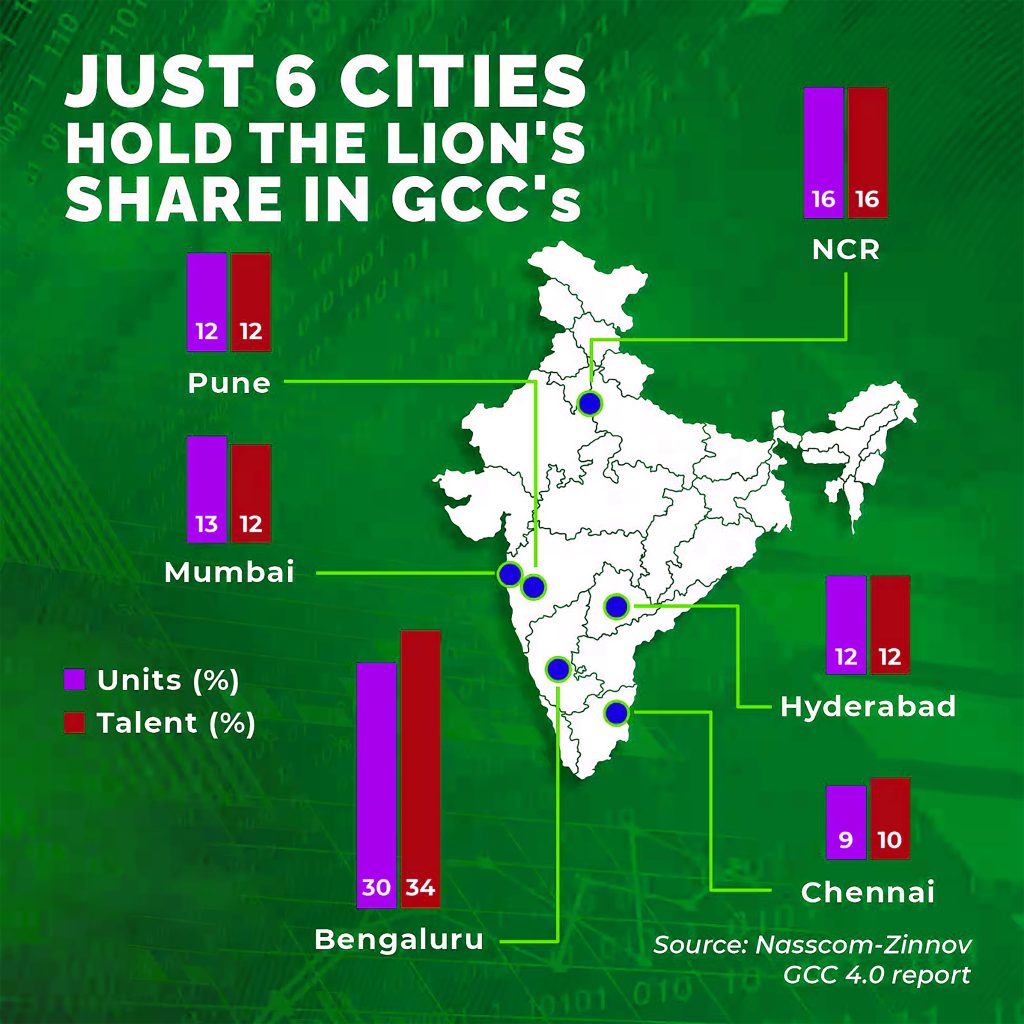
India has rapidly become the global capital for GCC operations, housing more than 1,600 centres as of 2024. These centres are critical to India’s economic transformation and are poised for exponential growth.
1. Employment Generation
As of FY24, GCCs in India employ nearly 2 million professionals, representing a dynamic blend of engineers, analysts, data scientists, and researchers. The sector continues to create high-quality employment opportunities for skilled talent.
2. Economic Contribution
The GCC ecosystem contributes an estimated USD 50 billion annually to the Indian economy, with this figure expected to rise as more MNCs establish operations in India. GCCs are pivotal in strengthening the country’s knowledge-driven economy and boosting foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows.
3. Infrastructure Development in Maharashtra
Under the newly approved Maharashtra GCC Policy, the state aims to double its GCC count from 400 to 800 by 2030. The policy targets ₹50,600 crore in fresh investments and the creation of four lakh new jobs.
The development of India’s first GCC city in Navi Mumbai is expected to serve as a model ecosystem—offering advanced digital infrastructure, sustainable urban design, and a global talent pool to attract leading enterprises.
4. Regional and Inclusive Growth
The Maharashtra policy also emphasises expanding GCCs to Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities, ensuring balanced regional development. Cities such as Pune, Nagpur, Nashik, and Aurangabad are likely to benefit from this decentralised approach, promoting innovation beyond metropolitan centres.
Why Maharashtra?
Maharashtra’s established industrial base, strong digital infrastructure, and global connectivity make it an ideal destination for GCC development. With Mumbai and Pune already serving as key technology and business hubs, the establishment of a GCC city in Navi Mumbai will further consolidate the state’s position as India’s economic powerhouse.
The state’s progressive policies, robust talent availability, and focus on innovation create an enabling environment for global enterprises to set up advanced operational centres that go beyond outsourcing.
Conclusion
The establishment of India’s first GCC city in Maharashtra marks a defining moment in the nation’s transition towards a high-value, innovation-led economy. By fostering global collaboration, generating employment, and promoting inclusive regional development, Maharashtra is setting a precedent for other states.
As GCCs evolve into strategic growth engines, they will continue to strengthen India’s reputation as a global hub for technology, innovation, and business excellence.
Subscribe to our Youtube Channel for more Valuable Content – TheStudyias
Download the App to Subscribe to our Courses – Thestudyias
The Source’s Authority and Ownership of the Article is Claimed By THE STUDY IAS BY MANIKANT SINGH





