Font size:
Print
Article 4 NATO Treaty
Context: The latest invocation of Article 4 by Poland in 2025, after Russian drones violated its airspace, highlights NATO’s growing reliance on consultations amid hybrid and drone warfare threats.
What is Article 4 of the NATO Treaty?
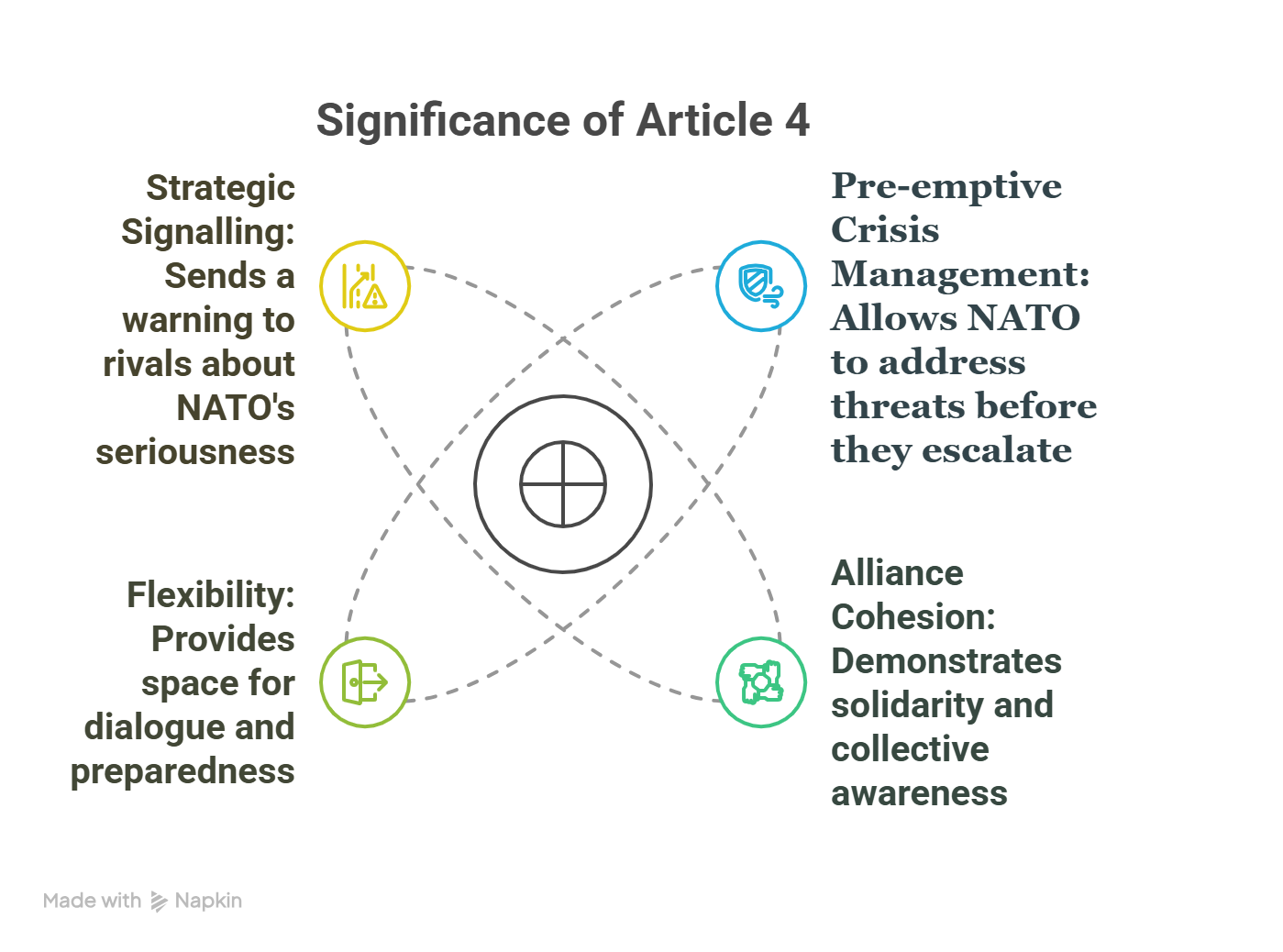
- Article 4 of the 1949 North Atlantic Treaty mandates consultations among allies if any member perceives a threat to its territorial integrity, political independence, or security.
- Unlike Article 5, which guarantees collective military defense, Article 4 is a diplomatic alarm bell ensuring coordinated responses without binding members to armed action.
- Past Invocations: Poland in 2014 (Crimea annexation), Eastern European allies in 2022 (Ukraine invasion), and most recently in 2025 after Russian drones breached Polish airspace. Turkey has also used it multiple times over border insecurities with Syria and Iraq.
Implications for India and Global Security Environment
- For India, not a NATO member, such developments highlight the fragility of the rules-based international order.
- As per the Economic Survey 2023–24, geopolitical shocks like the Russia–Ukraine war directly impact India’s energy security and food inflation. NATO’s consultations under Article 4 reflect how regional conflicts spill into global markets through disrupted supply chains.
- Globally, repeated Article 4 use signals a multipolar insecurity: Great-power rivalries, drone warfare, and blurred conflict boundaries. For India, this underscores the urgency of strategic autonomy—balancing Western partnerships (e.g., Quad) while safeguarding relations with Russia for defence and energy needs.
