Font size:
Print
The Vice-President of India
Context: Recently, C. P. Radhakrishnan has been elected as the 15th Vice-President. At a time when parliamentary functioning is often disrupted, the office of the Vice-President—as Rajya Sabha Chairman and potential Acting President—remains crucial for ensuring legislative order, political balance, and constitutional stability.
What are the main functions and powers of the Vice-President of India?
- The Vice-President of India is the second highest constitutional office after the President, defined under Articles 63–71 of the Constitution.
- Powers can be divided under 2 categories
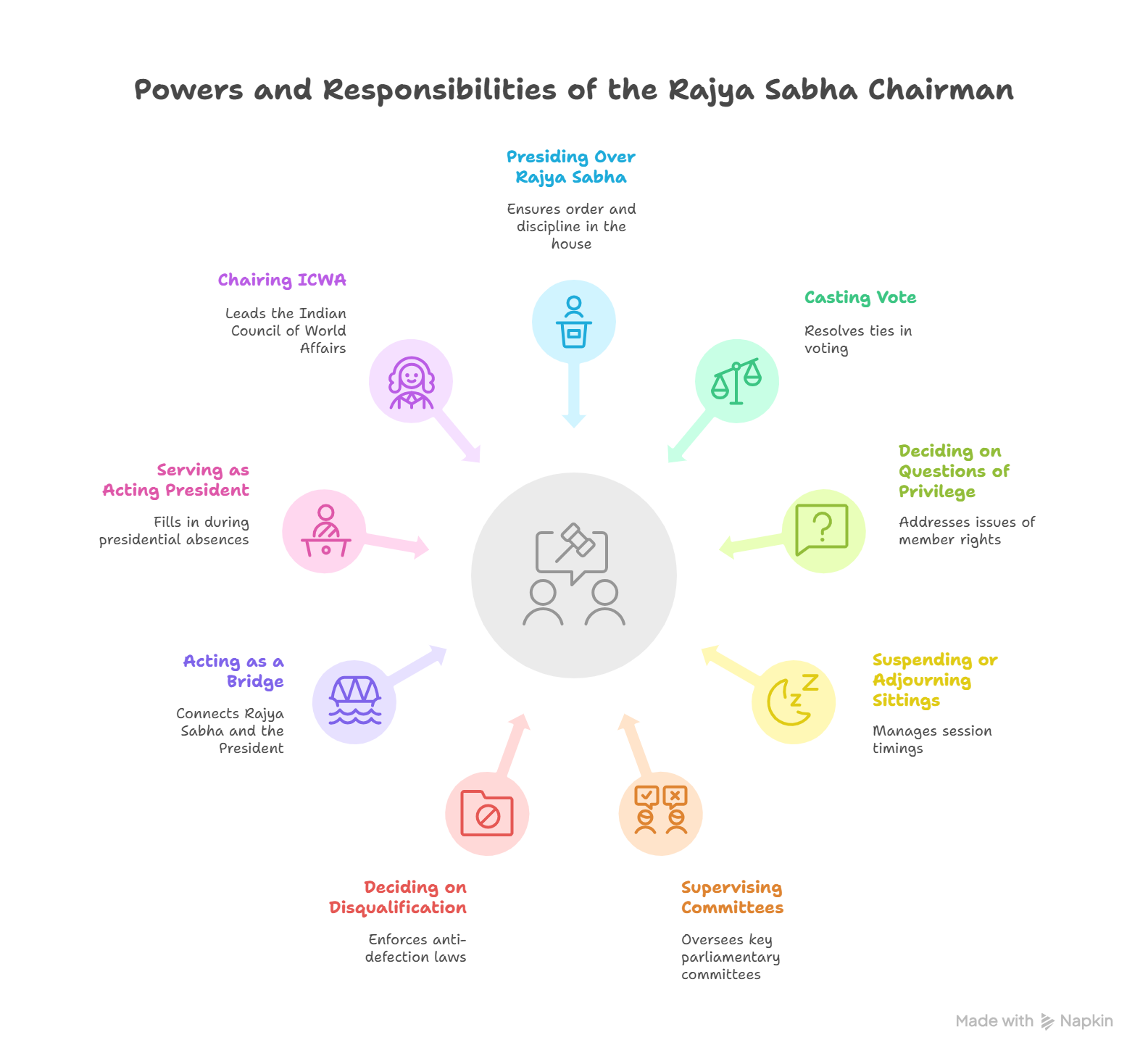
- As Ex-officio Chairman of Rajya Sabha (Article 64 & 89):
- Other Powers
- Thus, the Vice-President plays a dual role: parliamentary leadership and constitutional back-up to the President.
How is the Vice-President of India elected?
- The Vice-President is elected by an electoral college consisting of members of both Houses of Parliament (elected + nominated) through proportional representation by means of a single transferable vote (Article 66).
- The Election Commission of India conducts the election.
- Nominees must secure support from 20 proposers and 20 seconders among MPs.
- This system ensures representation across political parties and parliamentary strength.
How can the Vice-President be removed?
- Unlike the President, the Vice-President is not impeached but removed by a resolution of the Rajya Sabha (Article 67(b)):
- The resolution must be passed by a majority of all the then members of Rajya Sabha.
- It must be agreed to by the Lok Sabha.
- 14 days’ prior notice is required for introducing such a resolution.
- When such a resolution is under consideration, the Vice-President cannot preside over Rajya Sabha but may participate (without voting).
- No Vice-President has been removed so far, reflecting the stability of the office.
