Font size:
Print
Drug Menace in India: Urgent Challenges, Key Drivers, and Responses
Context: India’s escalating drug crisis has gained urgency with recent busts in Manipur and major seizures across Delhi, Gujarat, and Greater Noida, highlighting its dual role as a consumer and transit hub.
How prominent is the drug menace for India?
- India faces a growing narcotics crisis, both as a consumer and transit hub. The 2019 AIIMS–MoSJE survey estimated that 2% of Indians use opioids, marking one of the highest proportions globally.
- According to the Economic Survey 2022–23, drug trafficking drains resources, fuels crime, and undermines public health. In 2024 alone, Indian agencies seized narcotics worth over $1 billion, pointing to the scale of the underground economy.
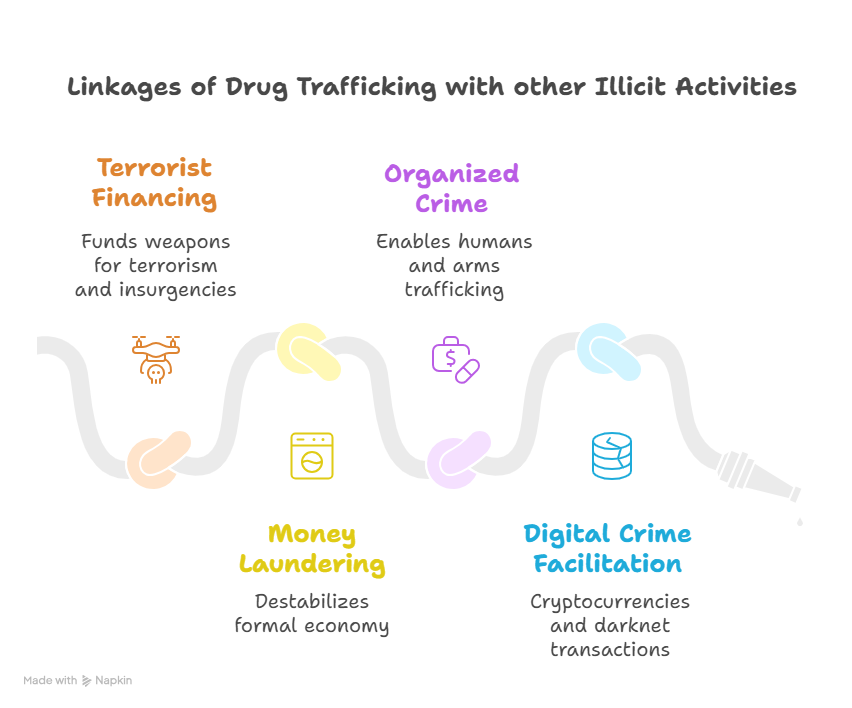
Which regions in India are more prone to it?
- Northeast India: Proximity to the Golden Triangle (Myanmar, Laos, Thailand) makes states like Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland vulnerable. The recent Imphal East and Thoubal seizures (2025) underline this.
- Punjab and Haryana: The AIIMS survey (2019) found Punjab had one of the highest opioid dependence rates, largely due to its location near the Golden Crescent (Afghanistan, Iran, Pakistan).
- Metros & Coastal States: Mumbai, Delhi, Goa, and Gujarat have seen rising cocaine and meth seizures, linked to international cartels.
What are the factors contributing to it?
- Geostrategic Location: India lies between the Golden Crescent and Golden Triangle, two of the world’s largest opium-producing regions.
- Youth Demographics: A large young population with rising disposable incomes makes for a growing consumer base (Down To Earth, 2023).
- Availability of Precursors: India’s pharmaceutical industry produces ephedrine and pseudoephedrine, which are often diverted to meth labs (UNODC 2023).
- Technology-enabled Trafficking: Darknet markets, crypto-payments, and drones have made detection harder.
What are the preventive countermeasures taken by India?
- Institutional Mechanisms: Establishment of NCB (1986) and a four-tier NCORD mechanism (2016) for inter-agency coordination.
- Legal Framework: Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985 (NDPS Act) empowers stringent action against traffickers.
- International Cooperation: India partners with UNODC and neighbours for cross-border operations.
- Awareness & Rehabilitation: The Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan (2020) operates in 272 districts, combining IEC campaigns with treatment facilities.
- Technological Measures: Use of satellite imagery, AI-based profiling at ports, and digitised case tracking systems.
Case Study: In Greater Noida (2024), authorities dismantled a meth lab linked to a Mexican cartel, showcasing India’s globalised drug challenges and law enforcement response.


