Font size:
Print
Data Sovereignty and National Security: A Critical Positive Shift for India
Data Sovereignty in India: A Powerful Driver of Strategic Autonomy
Data Sovereignty: With India implementing the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 and facing rising cyber threats from hostile neighbours, ensuring data sovereignty has become a strategic imperative to safeguard democracy, privacy, and economic autonomy.
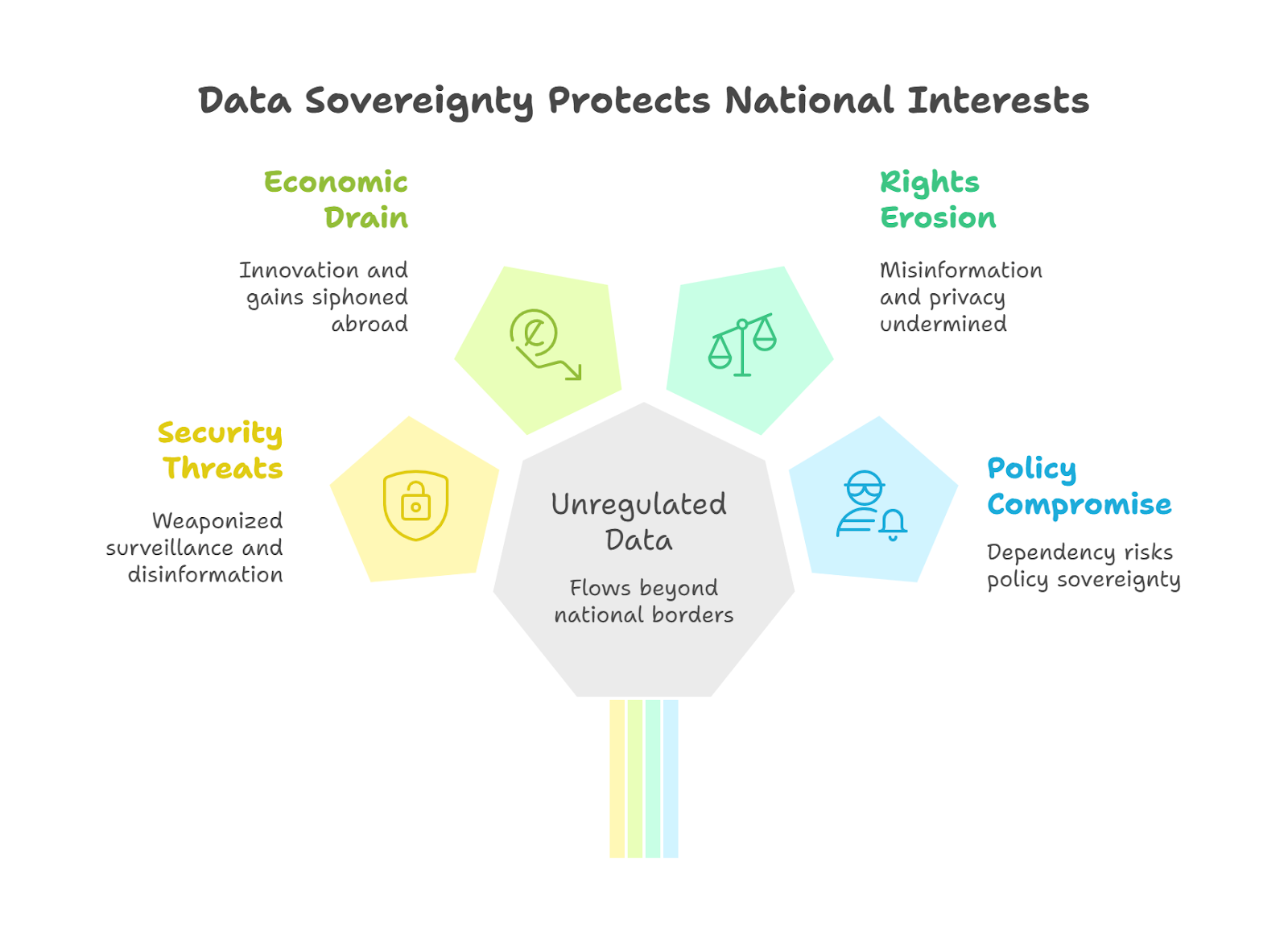
What is Data Sovereignty?
- Data sovereignty refers to the principle that digital data is subject to the laws and governance structures of the country where it is collected, stored, and processed.
- It implies that a nation exercises full authority over data generated within its borders, treating it as a strategic national resource akin to natural resources.
- The Economic Survey 2022-23 identified data as a “public good” essential for policymaking, innovation, and inclusive growth.
What measures have been taken to ensure Data Sovereignty?
- Legislative Initiatives
- Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023 – establishes consent-based data processing and mandates obligations on fiduciaries. However, it is yet to be fully operationalised.
- IT Act, 2000 (amended 2008) – provides a legal framework for cyber security and electronic governance.
Case Study: Aadhaar Ecosystem
India’s Aadhaar project, covering over 1.3 billion residents, showcases both potential and risks. While enabling direct benefit transfers and financial inclusion (Economic Survey 2020-21), it also highlighted vulnerabilities around privacy, leading to the Supreme Court’s Puttaswamy Judgment (2017) that affirmed privacy as a fundamental right.
- Draft National Data Governance Framework Policy (2022) – aims to enable secure access to non-personal data for public good.
- Institutional Mechanisms
- Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) monitors cyber threats and mandates reporting of data breaches.
- National Cyber Security Policy (2013) provides a roadmap for protecting critical information infrastructure, though an updated version is awaited.
- Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) monitors cyber threats and mandates reporting of data breaches.
- Global and Comparative Practices
Subscribe to our Youtube Channel for more Valuable Content – TheStudyias
Download the App to Subscribe to our Courses – Thestudyias
The Source’s Authority and Ownership of the Article is Claimed By THE STUDY IAS BY MANIKANT SINGH



