Font size:
Print
India’s Insurance Sector
Context: The 2025-26 Union Budget raised the Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) cap in insurance to 100%, building on the 2021-22 hike to 74%.
More on News
- However, Finance Ministry data (December 2024) reveals only 4 out of 19 life insurers and 0 out of 20 general/health insurers utilised even the 74% limit.
- This tepid response highlights structural challenges in India’s insurance sector, despite its projected 7.1% annual growth.
Insurance penetration is the ratio of total insurance premiums (life + non-life) to a country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP), expressed as a percentage. Insurance density is defined as the per capita premium (insurance premium per person) in a country, usually expressed in USD.
What are the Major Challenges in India’s Insurance Sector?
- Low Penetration & Awareness: Insurance penetration stagnates at 4.2% of GDP (life: 3.2%, non-life: 1.0%), far below global averages (IRDAI Annual Report 2023-24).
- Rural-urban divide: Only 30% of rural households have insurance coverage (NITI Aayog, 2024).
- Capital Infusion & Solvency Pressures: High claim ratios (life: ~90%, health: ~110%) strain profitability.
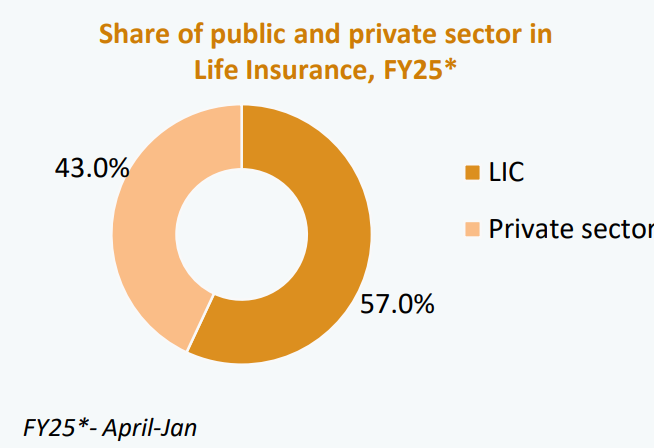
- Public insurers (LIC, GIC) dominate with 64% market share, crowding out private players.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Delayed approvals for product launches and FDI inflows (World Bank Ease of Doing Business 2023).
- Taxation disputes, e.g., GST on reinsurance premiums, deter foreign reinsurers (NITI Aayog, 2023).
- Consumer Trust Deficits: Mis-selling and claim settlement delays erode confidence.
How Raising FDI Limit Can Address Challenges?
- Capital & Technology Infusion: Global insurers (e.g., Allianz, Prudential) can bring long-term capital and AI-driven underwriting tools (NITI Aayog, 2024).
- Example: Zurich Insurance’s 70% stake in Kotak General improved solvency margins by 15% (Finance Ministry Data).
- Enhanced Competition & Innovation:
-
- Product diversification: Foreign players may introduce micro-insurance and parametric weather insurance for farmers (Economic Survey 2023-24).
- Lower premiums through economies of scale (IMF Country Report 2024).
- Improved Penetration: Foreign expertise can expand distribution via digital platforms and last-mile agents (IRDAI 2024).
What are the Other Measures to Tackle Insurance Sector Issues?
- Regulatory Reforms:
-
- IRDAI’s Bima Trinity Initiative (2024):
-
-
-
- Bima Sugam: Single portal for policy comparison/grievance redressal.
- Bima Vistar: Composite risk cover for rural households.
-
-
- Fiscal Incentives:
-
- Tax deductions for premiums paid (enhance 80D limit to ₹1 lakh).
- GST rationalisation on reinsurance (NITI Aayog, 2023).
- Public-Private Synergy: LIC’s infrastructure investments to be mirrored by private insurers.
- PSU insurer reforms: Reduce government stakes in GIC and New India Assurance (RBI Report 2024).
- Awareness Campaigns:
-
- Jan Bima Yojana: Nationwide drive for term insurance awareness (Budget 2025).
