How to Integrate Old and New NCERTs for Ancient History (UPSC)
A detailed UPSC preparation guide on how to effectively integrate Old NCERTs (R.S. Sharma) with New NCERTs (Themes in Indian History) to cover Ancient Indian History comprehensively.
Introduction: Old & New NCERTs

Ancient Indian History is a vital part of both UPSC Prelims and Mains. NCERTs—both old and new—have always been a trusted source of preparation. However, aspirants often face a dilemma:
“Should I rely on the old NCERTs for Ancient History because they are rich in facts, or use the new NCERTs that are thematically structured and conceptually deep?”
The ideal approach is to combine the strengths of both, and this article guides you through how to do exactly that—step by step.
Importance of NCERTs in UPSC Preparation
- NCERTs form the conceptual foundation for further studies.
- They provide authentic, factually correct, and exam-relevant information.
- Many questions in UPSC Prelims and Mains are directly or indirectly derived from NCERT content.
- They help in developing a timeline-based understanding and in creating well-organised notes.
Why Combine Old and New NCERTs?
The Old NCERTs, especially R.S. Sharma’s “Ancient India”, are known for their analytical approach. They explain historical developments through socio-economic and political lenses—perfect for GS Paper I Mains. The New NCERTs, such as Class 6’s “Our Pasts – I” and Class 11’s “Themes in Indian History Part I,” present topics in simple language, with visually enriched layouts and summaries that help in quick Prelims revision. By integrating both, aspirants can achieve a balanced understanding—with the Old NCERTs offering depth and the New NCERTs offering structure and clarity.
What to Use from the New NCERTs?
The New NCERTs are ideal for beginners and structured preparation. For instance, Class 6’s “Our Pasts – I” introduces early human life, Harappan civilization, and Vedic culture in easy language suitable for new learners. Class 11’s “Themes in Indian History Part I” is directly aligned with the UPSC syllabus. It covers topics like religious developments, political formations, and Mauryan and post-Mauryan empires with thematic insights. These books also contain maps, timelines, and visuals, which are especially helpful for solving map-based or chronological MCQs in Prelims.
Benefits of Using the Old NCERTs (R.S. Sharma)
1. Factual Richness
The old NCERT, especially Ancient India by R.S. Sharma, contains exhaustive information. It includes detailed discussions on political dynasties, administration, economy, religion, society, and architecture.
2. Exam-Oriented Content
The language is concise and to the point, making it easier for quick revision and memorisation. It is especially useful for UPSC Prelims, where factual recall is crucial.
3. Chronological Flow
It follows a clear and logical progression, from prehistoric times to early medieval India, helping aspirants build a timeline-based understanding.
4. Emphasis on Socio-Economic Aspects
The book goes beyond dynasties and kings—it also focuses on land systems, taxation, trade, craft production, and class structures, which are useful in analytical answers.
Strengths of the New NCERTs (Themes in Indian History Part I)

1. Thematic and Analytical
The new NCERT follows a theme-based structure, dealing with broad ideas such as “The Harappan Civilisation,” “Early States,” or “Religious Developments.” This helps in understanding processes and transitions in Indian history.
2. Updated with New Findings
It includes recent archaeological and historical interpretations, such as new findings on Harappa, reinterpretations of the Mauryan administration, and updated views on Buddhism and Jainism.
3. Conceptual Clarity
The content is designed to enhance critical thinking, focusing not only on ‘what happened’ but also on ‘why it happened’ and ‘how it influenced society.’
4. Use of Source Material
It includes visual sources, inscriptions, coins, and excerpts from original texts, which are highly relevant for UPSC Mains to substantiate answers.
How to Combine Both NCERTs Effectively
Step 1: Begin with the Old NCERT (R.S. Sharma)
- Use it to create a strong factual base.
- Note important dates, places, dynasties, administrative systems, and economic practices.
- Make timeline charts and tabular summaries from each chapter.
Step 2: Read the Corresponding Chapters in the New NCERT
- After reading a topic in the old NCERT, read its theme in the new NCERT to get deeper context.
- Understand the processes behind historical developments, such as the decline of Harappan civilisation or the spread of Buddhism.
Step 3: Prepare Comparative Notes
This comparative framework helps in consolidation and interlinking of facts with ideas.
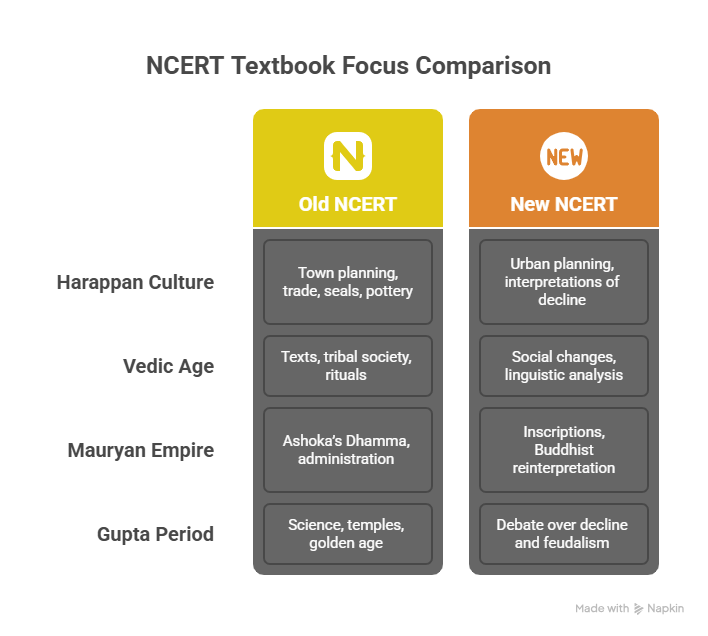
Authentic Examples of Integration
Let’s consider the topic of Jainism and Buddhism. The New NCERT presents these religions through their core teachings and spread across India, helping students memorise key facts. On the other hand, R.S. Sharma deals with the causes behind their rise, such as social discontent under Brahmanism, and their patronage by urban merchants. Combining both helps in framing answers that are both factually correct and analytically rich.
Another example is Vedic Literature. The New NCERT categorizes Rigvedic and Later Vedic periods with cultural traits. The Old NCERT explains the changing social structure, emergence of caste, and early state formations—crucial for understanding historical progression.
Tips for Making Notes from Both NCERTs
- Use the old NCERT for creating short notes and bullet points on kings, battles, timelines, economic systems, etc.
- Use the new NCERT for analytical notes, such as reasons for urbanisation, patterns of religious change, or debates among historians.
- Highlight primary sources (like Ashokan edicts or Sangam literature) for use in Mains answers.
- Keep revising your notes after each stage of integration.
UPSC-Specific Advantages of Integration
For Prelims
- Factual knowledge from old NCERT improves accuracy in objective questions.
- Helps in identifying trick questions, where minor factual errors are used to confuse aspirants.
For Mains
- Analytical depth from the new NCERT enhances the quality of descriptive answers.
- Helps in writing balanced perspectives by combining factual evidence with interpretation.
For Essay & Interview
- The new NCERT gives a historical viewpoint on social issues, helping with essays on culture, religion, or philosophy.
- Quotable materials from sources like Rigveda or Arthashastra add value in the interview stage.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Reading only one of the two NCERTs – This limits either your factual depth (if reading only new) or your analytical ability (if reading only old).
- Reading them cover to cover without selection – Focus only on UPSC-relevant chapters. Skip repetitive or less relevant portions.
- Making notes without integration – Merge facts from old NCERT with analysis from the new NCERT to avoid duplication.
List of Recommended Chapters (Old vs New NCERT)

Conclusion
Aspirants preparing for UPSC must move beyond the debate of old vs new NCERTs and adopt a smart strategy that combines the factual strength of the old NCERTs with the analytical depth of the new ones. This integrated approach will not only ensure holistic preparation but also enhance your ability to think critically, write effectively, and perform confidently in all stages of the UPSC exam.
Subscribe to our Youtube Channel for more Valuable Content – TheStudyias
Download the App to Subscribe to our Courses – Thestudyias
The Source’s Authority and Ownership of the Article is Claimed By THE STUDY IAS BY MANIKANT SINGH





