Font size:
Print
The US AI Diffusion Framework
US AI Diffusion Framework for Global AI Regulation
Context: The United States AI Diffusion Framework, introduced in January 2025, is a strategic attempt by Washington to regulate the global spread of AI technology and curb China’s technological ascendancy. This framework represents a critical inflection point for countries like India, aiming to expand their AI infrastructure amidst evolving export control regimes.
Salient Features of the US AI Diffusion Framework
- Objective of the Framework
- To preserve US global leadership in AI compute by restricting access to advanced AI chips, cloud services, and model weights.
- Designed to limit China’s access to key AI resources and prevent indirect re-exports.
- Regulation of AI Model Weights
- For the first time, export restrictions have been applied to AI model weights.
- Threshold set at 1026 FLOPS for training—excluding most current open-source models like GPT-4.
- The threshold is dynamic and will evolve with model development.
- Revised Licensing Regime for AI Chips
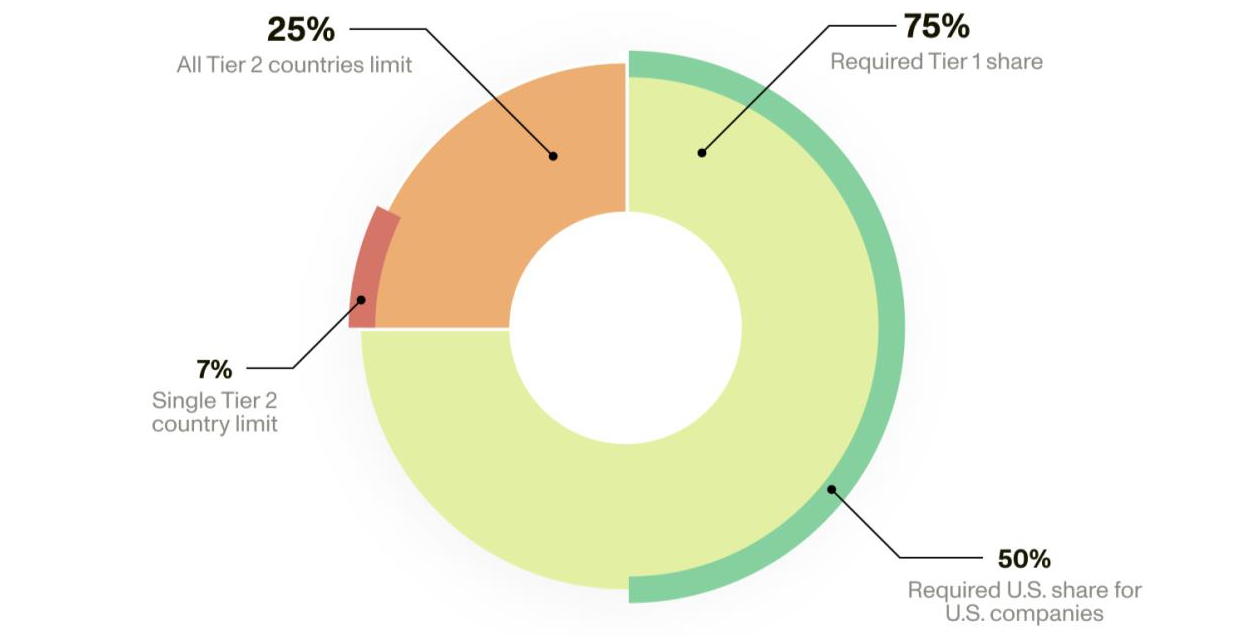
- Tier-based access system for AI infrastructure:
- Tier 1: Unrestricted access for 18 major US allies (e.g., Japan, UK, Taiwan).
- Tier 2: Includes most countries (including India); subject to controls.
- Tier 3: US arms-embargoed nations (e.g., China, Russia, North Korea); banned from access.
- Tier-based access system for AI infrastructure:
- Data Center Access: UVEU and NVEU Mechanism
- Updated DC VEU Programme
- Introduced bifurcation:
- Universal Validated End Users (UVEUs) – Accessible only to Tier 1 firms for deployment in Tier 2.
- National Validated End Users (NVEUs) – Tier 2 companies must seek separate authorisation per country.
- Security Protocols and Enforcement Measures
- Stringent cybersecurity, physical, and personnel protocols to avoid:
- Theft of chips,
- Unauthorised access,
- Illegal chip transfers to Tier 3 nations.
- The US Commerce Department has proactively notified major chipmakers like TSMC and Samsung to enforce compliance.
- Stringent cybersecurity, physical, and personnel protocols to avoid:
Global Implications of the Framework
- Short-Term Impact
- Tier 1 nations (e.g., Australia) will benefit from liberal access and rising investments.
- Tier 2 nations, particularly Southeast Asian economies (Malaysia, Singapore), will face:
- Delayed access to critical compute,
- Investment slowdowns due to overlapping US-China interests.
- Long-Term Implications
- The US will consolidate global leadership in AI computers.
- Countries will be increasingly locked into US ecosystems due to:
- China’s lagging GPU technology (e.g., Huawei Ascend series),
- Software and ecosystem incompatibilities.
India’s Position and Emerging Challenges
- Current Scenario
- India is a Tier 2 country, aspiring to emerge as a global AI hub.
- The National AI Mission targets over 10,000 GPUs over the next 5 years.
- Projects like Reliance’s 3 GW AI mega data centre in Gujarat are aligned with this ambition.
- Challenges Under the Framework
-
- NVEU authorisation is now a precondition for AI chip access.
- Need for compliance with tight US security protocols.
- Risk of being affected by illegal re-exports (e.g., allegations of AI chip smuggling to Russia via India).
- Global push towards compute efficiency and open-source models like DeepSeek from China may rise—but still require US chips.
Recommendations for India: Strategic Pathways
- Secure NVEU Authorisation Proactively
- Indian firms must focus on:
- Meeting cybersecurity and supply chain norms,
- Severing links with Chinese partners,
- Preventing illicit chip re-export (e.g., to Russia).
- Indian firms must focus on:
- Diversify Compute Strategy: Emphasise Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) and Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) to reduce dependency on top-tier GPUs.
- Prioritise National Allocation of GPUs
- Create a centralised system for GPU allocation based on national priorities, not private demand.
- Establish first-come, first-served procurement mechanisms for AI chips.
- Build Regional AI Corridors
- Collaborate with like-minded Tier 2 countries to:
- Pool computing resources,
- Create cross-border AI corridors and shared R&D facilities.
- Collaborate with like-minded Tier 2 countries to:
- Invest in Efficient Open-Source Models
- Develop low-compute large language models through public-private partnerships.
- Learn from China’s DeepSeek and lead efforts in compute-efficient innovation.
- Strengthen Bilateral Cooperation with the US
- Expand initiatives like:
- US-India Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET),
- Tata-Micron semiconductor plant for chip packaging and testing.
- Seek government-to-government assurances to smoothen NVEU access.
- Expand initiatives like:

